© HeiQ RAS AG
ELa
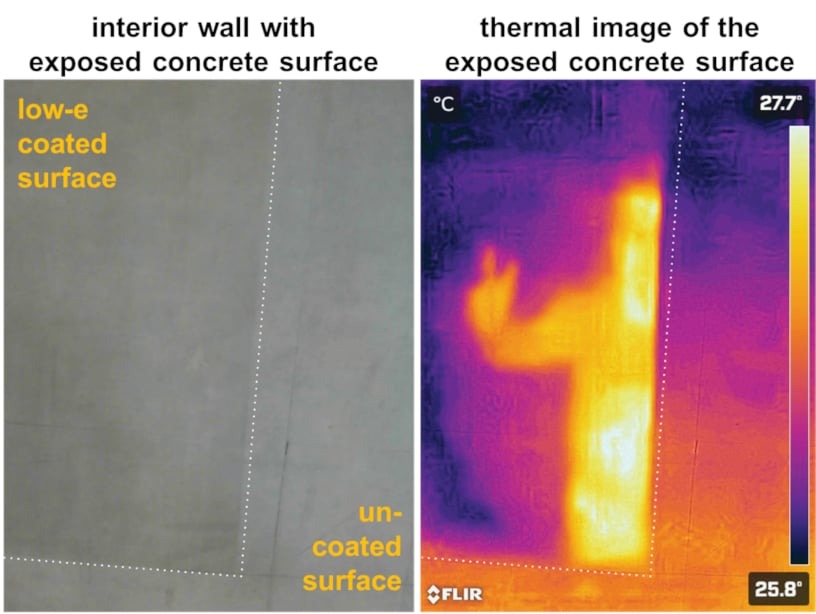
Energy-saving glaze with stabilized silver nanowires for transparent low-e wall coatings
The aim of the project is to develop a transparent, low-emissivity (low-e) energy-saving glaze based on stabilized silver nanowires. This glaze can improve the insulation performance of buildings by up to 25% with virtually no change to the visual appearance of the color, by significantly reducing heat radiation from wall surfaces due to its low emissivity. For this purpose, the glaze is specifically applied to the interior side of exterior walls (exposed concrete, plaster, etc.), particularly in older buildings.
The resulting product, which is to be marketed in the future under the name HeiQ Xpectra by the project partner HeiQ RAS AG, received the “German Sustainability Award 2026” for products in the Climate Transformation field. The award recognized its “[…] ability to make a significant contribution to energy savings and emission reductions with minimal material use and effort […]”.
Funding body: BMFTR, funding code: O3DPS12O8A
Duration from 01.09.2024 to 28.02.2026


