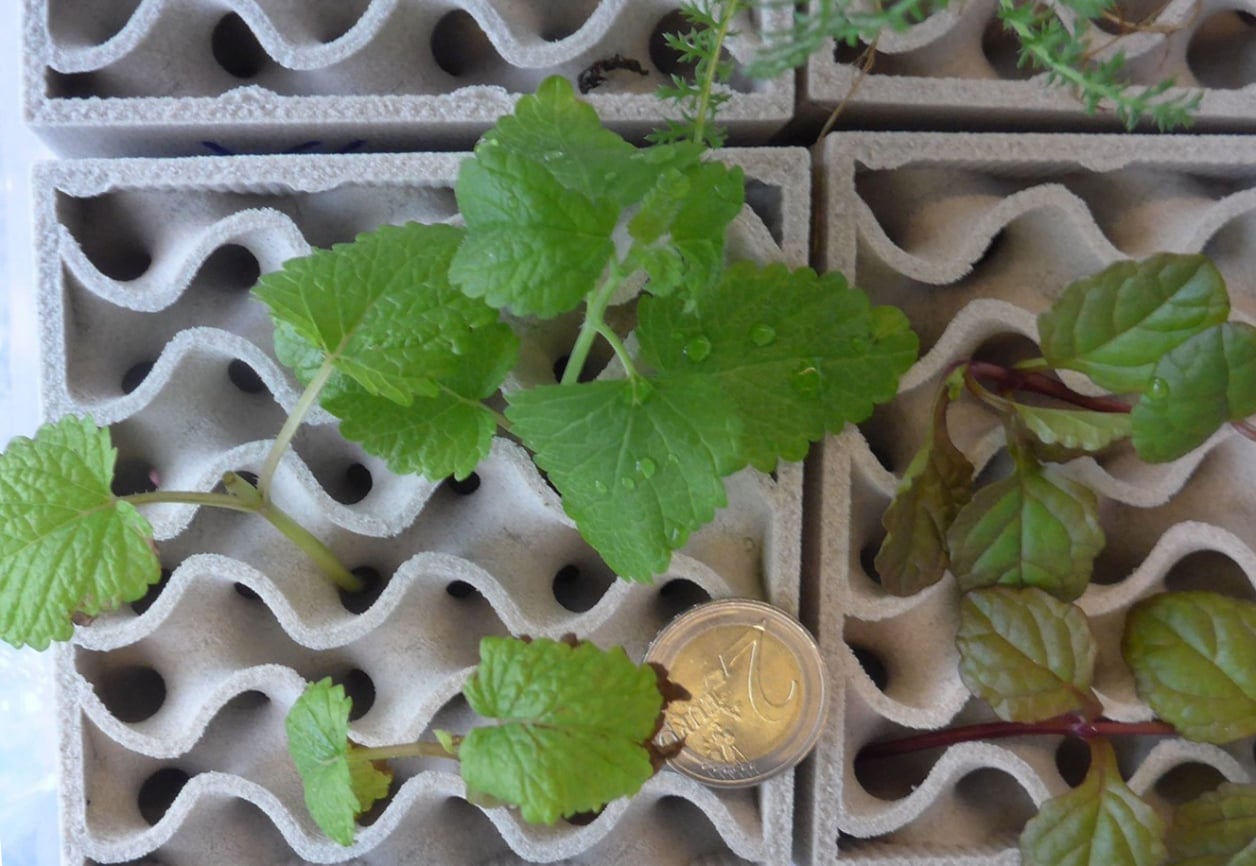
symbiosis(System made of mineral material with self-sustaining biological growth and thermally insulating)
Development of a new type of façade greening with an optimized insulating effect, which is self-sufficient via a capillary water reservoir. The entire system is laser-sintered from a perlite and printed in corresponding functional layers using a 3D printer. This takes place in a pilot plant at the project partner ING3D GmbH. Using a 2000 W laser in a unique and innovative 3D manufacturing process known as “Mineral Direct Laser Sintering” (MDLS), the additive manufacturing of extremely lightweight and non-combustible objects is being realized for the first time. The mineral raw material used in this process makes 3D printing more than 10 times faster than conventional 3D printing processes (e.g. plastic printing) and can therefore be used for industrial production.
The aim of this micro-project is to evaluate the potential of 3D-printed porous structures as a basis for façade greening. Gradient materials with variable porosity are to be printed and examined with regard to their material properties. Growth and rooting tests will demonstrate the suitability of the structures for the growth of selected plants. Conversely, different plant species will be tested for their suitability to grow on the printed structures.
Funding body: BMWE, funding code: 09ENM1001
Duration from 01.12.2024 to 30.09.2025